Building a phased roadmap for equipment digitization rollouts
A phased roadmap helps manufacturers convert manual and legacy equipment into connected assets methodically. This approach balances immediate operational needs with long-term digitization objectives, reducing disruption while unlocking benefits like predictive maintenance, improved quality control, and energy transparency. A clear, staged plan guides resource allocation, risk management, and measurable KPIs across the rollout.

manufacturing: what are the goals?
Before retrofitting equipment, clarify manufacturing objectives for digitization. Define performance targets such as reduced downtime, improved quality, or faster throughput, and map them to measurable KPIs. Consider where digitization will deliver the most value—assembly lines, process cells, or logistics flows—and pilot in a contained area. Engage operations, engineering, and procurement early and consult local services for on-site integration expertise. Establish governance that connects shop-floor metrics to corporate reporting so manufacturing improvements are visible and actionable across teams.
automation and iot: where to start?
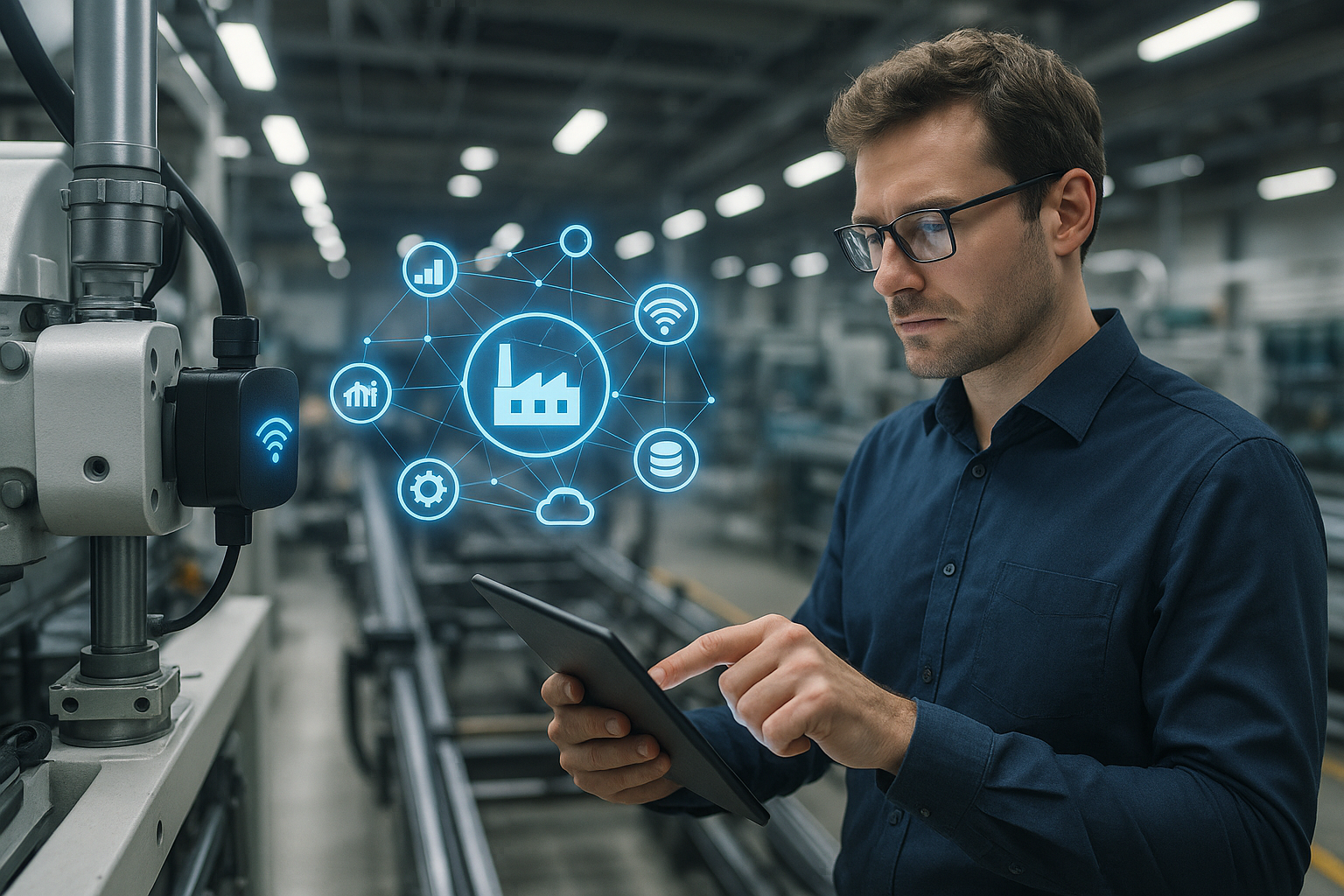
Start by identifying which automation systems and IoT endpoints are feasible to connect in early phases. Prioritize equipment with digital control interfaces or those that can accept IoT gateways without invasive changes. Plan phased integration: phase 1 focuses on non-critical monitoring, phase 2 covers control optimizations, and phase 3 enables closed-loop automation. Ensure digitization roadmaps include hardware lifecycle plans, spare parts, and vendor interoperability so automation upgrades align with maintenance and procurement cycles.
sensors and analytics: what data matters?
Select sensors that capture data tied to KPIs—vibration and temperature for rotating equipment, pressure and flow for process lines, or vision systems for quality checks. Define a data model that standardizes naming, units, and timestamps across assets. Analytics pipelines should transform raw sensor feeds into actionable insights: anomaly detection, trend analysis, and KPI dashboards. Start with simple analytics and iterate; early wins from basic thresholds or simple statistical models build confidence for more advanced predictive analytics later.
maintenance and quality: phased approaches
Digitization can reshape maintenance from reactive to predictive and support consistent quality control. In phase 1, implement condition monitoring for critical assets to reduce unexpected failures. Phase 2 adds predictive maintenance models informed by analytics, historical logs, and sensor fusion. For quality, introduce inline inspection sensors and automated feedback loops that flag deviations and route corrective actions. Integrating maintenance and quality data enables root-cause analysis that reduces rework and aligns asset health with product specifications.
energy, sustainability and logistics planning
Digitization supports energy monitoring, emissions tracking, and more efficient logistics. Begin with energy submetering on major equipment and capture usage patterns. Use analytics to identify peak loads and opportunities for load shifting or equipment scheduling to reduce consumption. For sustainability, digitize data required for reporting and continuous improvement. In logistics, integrate equipment status with material flow and inventory systems so digitized assets communicate availability and reduce delays in internal transport and scheduling.
cybersecurity, cloud and twinning integration
Protecting connected equipment is foundational to a phased rollout. Implement network segmentation, secure device onboarding, and endpoint hardening from the outset. Use cloud services for scalable data storage and analytics but design hybrid architectures when latency or data residency demands it. Consider digital twinning for complex assets or lines to simulate changes before deployment; start with lightweight virtual models and evolve fidelity as confidence grows. Security reviews, firmware management, and incident response play a continuous role across all phases of digitization.
Conclusion
A phased roadmap for equipment digitization balances quick operational improvements with longer-term transformation. By prioritizing pilots, selecting meaningful sensors, aligning analytics to KPIs, and integrating maintenance, energy, and logistics data, organizations can build capability incrementally. Embedding cybersecurity, cloud strategies, and twinning early ensures resilience and scalability as digitization moves from isolated rollouts to enterprise-wide adoption.